Welcome to the world of sugar free joy!
Low Carb Sugar-Free Desserts & Snacks
Artinci was born out of Aarti's and Sumit's (Artinci's founders) abiding love for great-tasting dessert, while helping them stay committed to their health goals as well. As a result, Artinci makes delicious desserts with zero sugar, that are science and evidence-backed.
Aarti and Sumit come from a family of three generations of diabetics. They were themselves diagnosed pre-diabetic in 2012, and right there began a lifelong quest of a healthy, active lifestyle, including healthy swaps in food
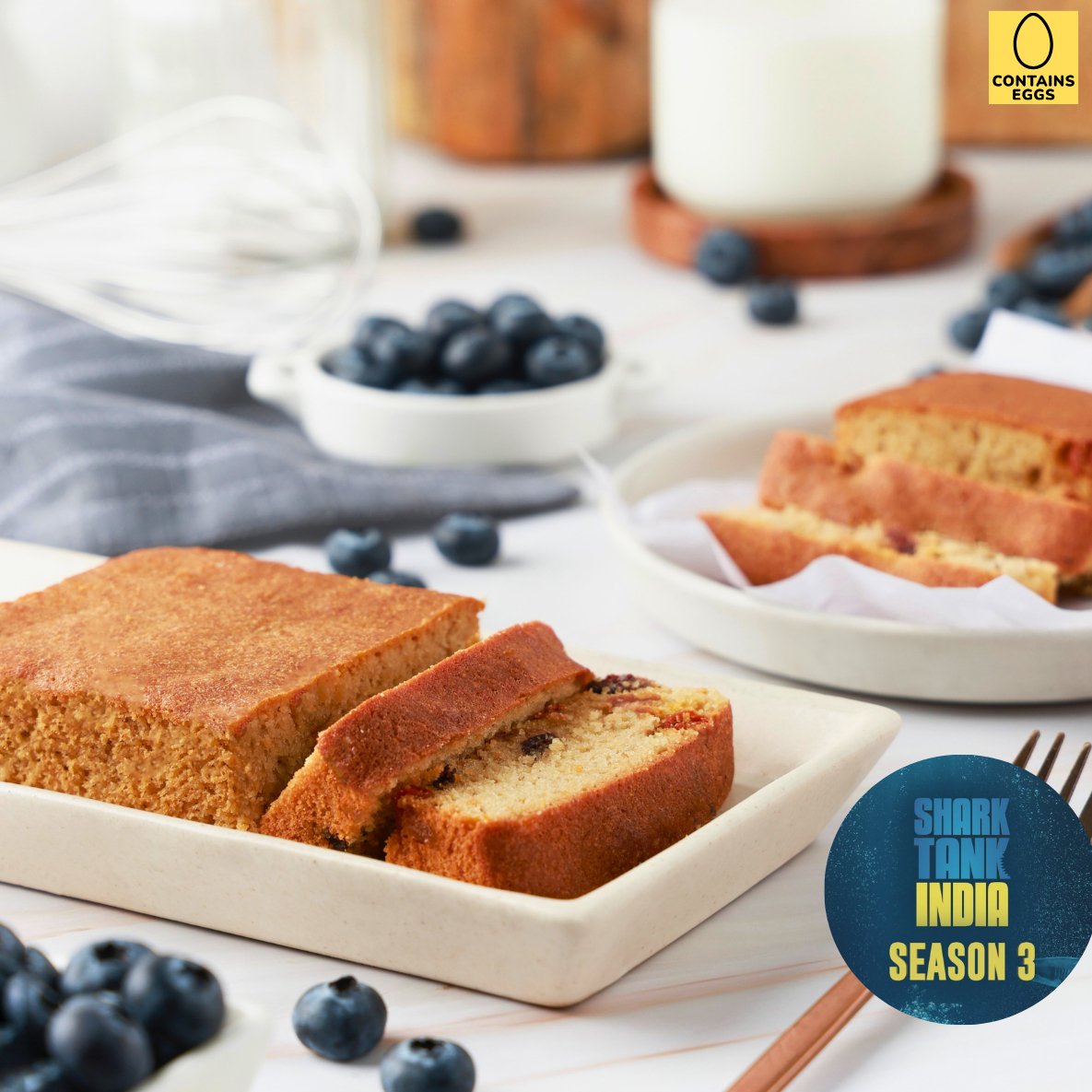
Indulgent Halwas & Cozy Cakes





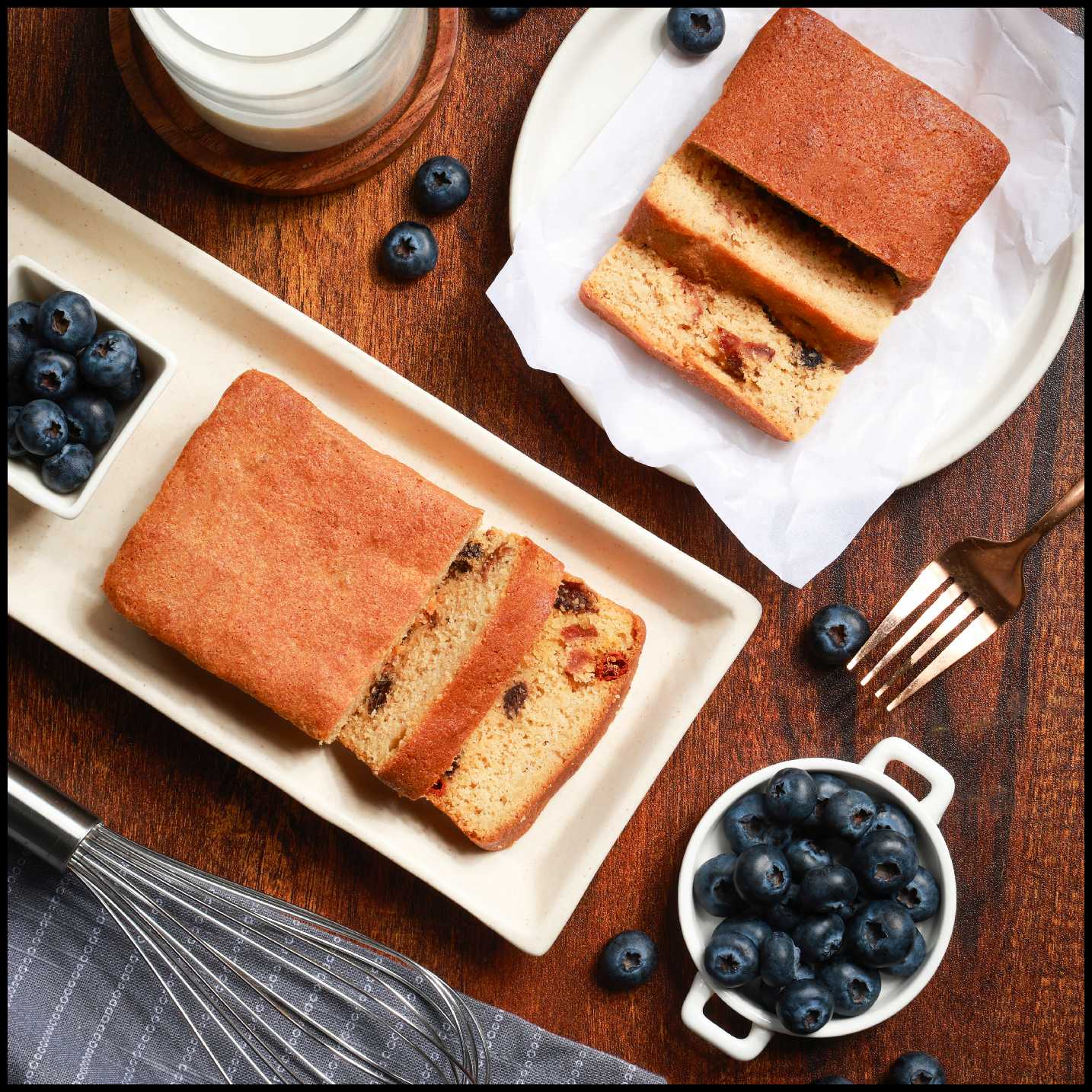
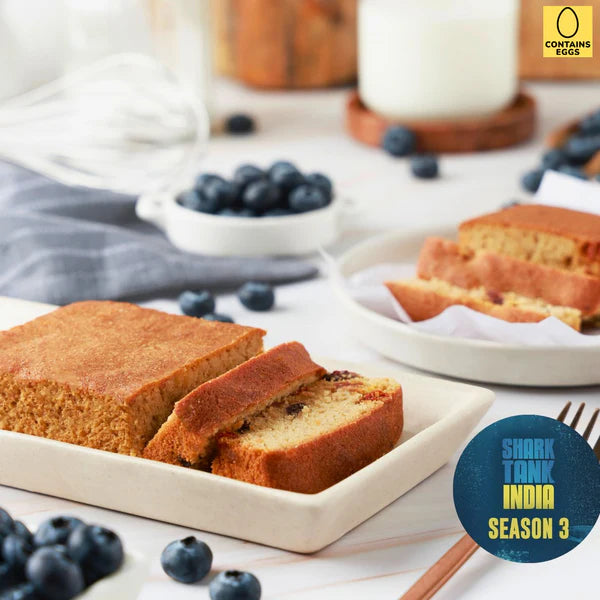
Berries Almond Cake - Made with 100% Almond Flour, Sugar Free, Keto, Gluten Free



Winter special sugar free halwa combo @499


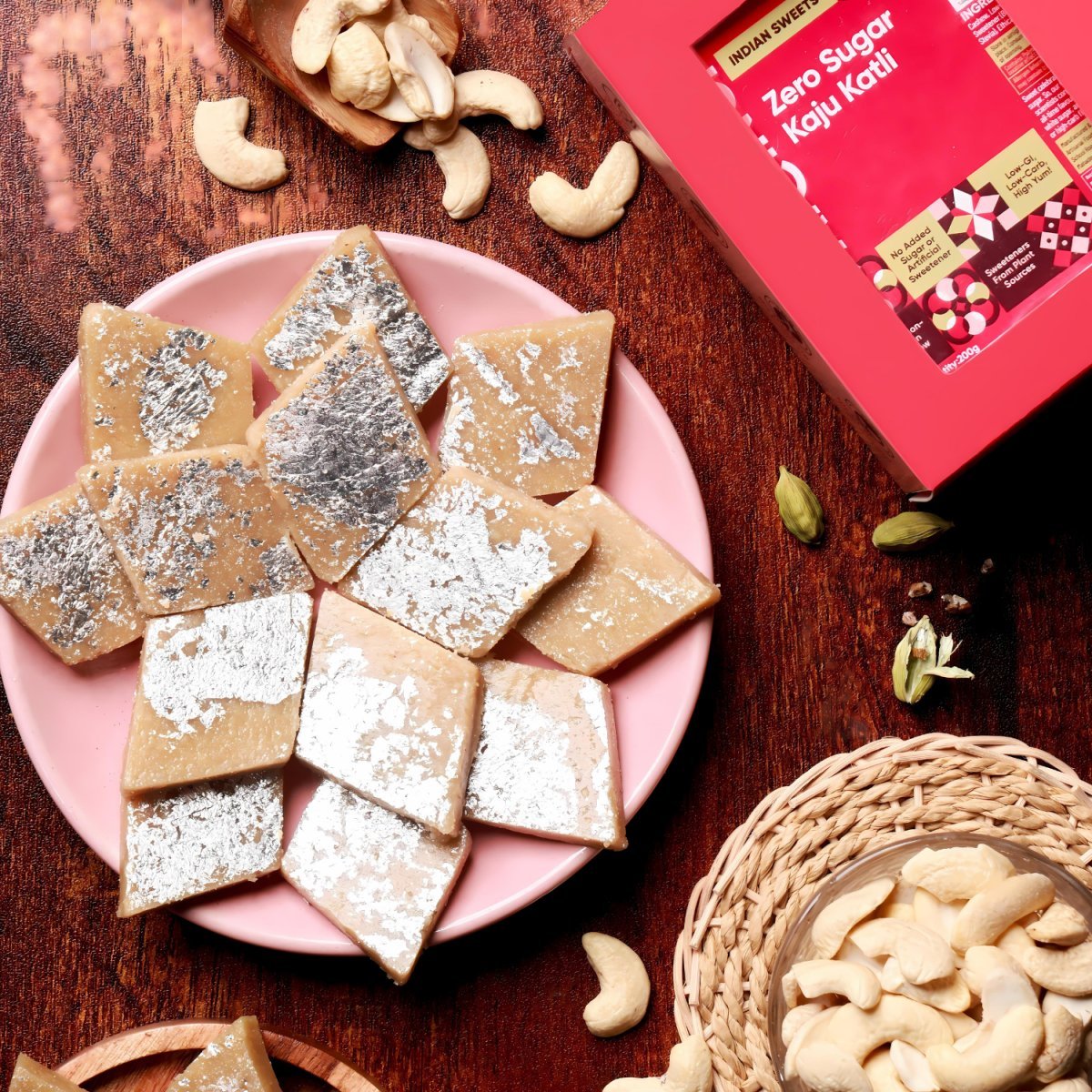
Valentine Gifting in Artinci
Let customers speak for us
Latest Suger free Tips

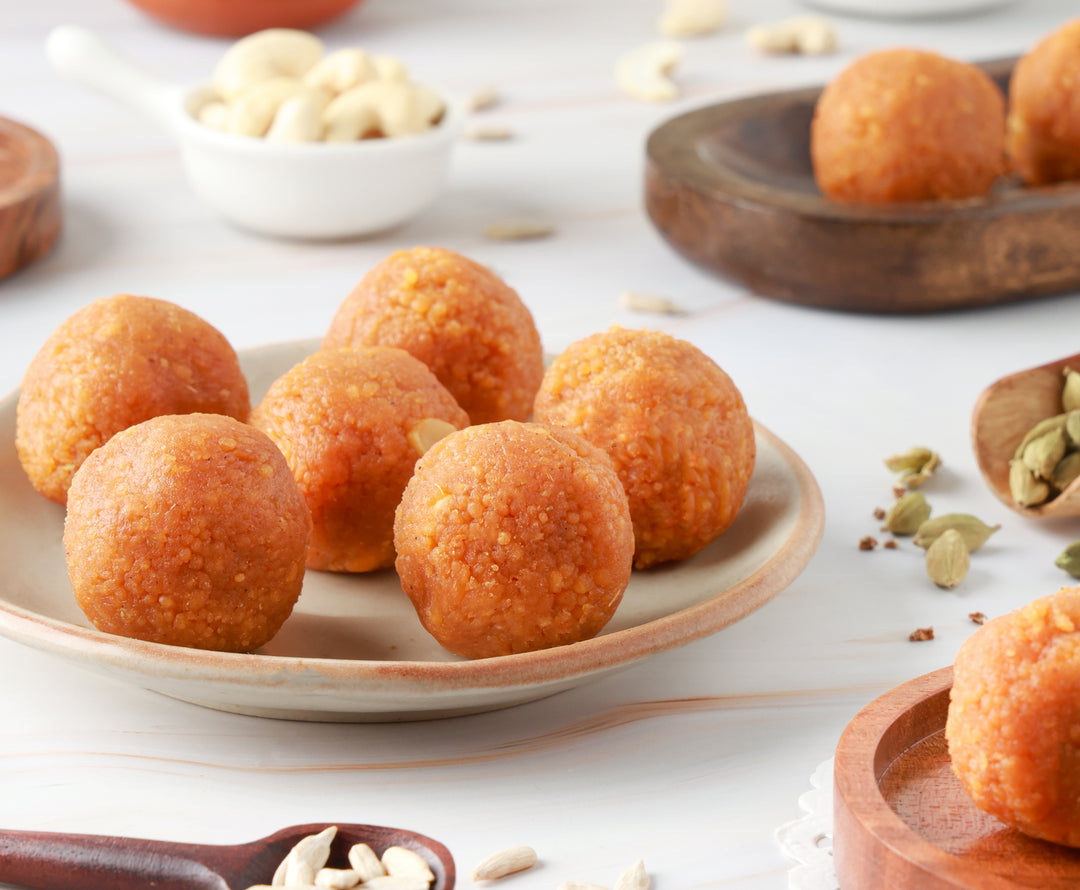
Introduction Your skin reveals a lot about your diet, especially how much sugar you consume. Studies show that there's a direct link between eating sugar and various skin problems like aging and acne. The food you eat is crucial for maintaining healthy, glowing skin. When you understand how your diet affects your skin, you can make better choices about what to eat. Research indicates that the meals you have directly influence your skin's appearance and health. Cutting sugar from your diet isn't just about weight management - it's a powerful step toward achieving healthier, more vibrant skin. Many people report significant improvements in their skin's appearance within weeks of reducing their sugar consumption. However, managing sugar intake can be challenging, especially for those with conditions like diabetes. You can start by replacing sugary treats with Diabetic friendly sugar-free sweets to satisfy your sweet cravings while protecting your health. These delicious alternatives let you enjoy desserts guilt-free while keeping your sugar intake in check. The Negative Effects of Sugar on Skin Health Sugar's impact on your skin extends far beyond temporary breakouts. Research reveals a direct connection between high sugar consumption and persistent skin issues through multiple biological mechanisms. Inflammation Your body responds to excessive sugar intake by triggering inflammatory responses. This systemic inflammation manifests in your skin through: Persistent redness and irritation Increased acne breakouts Flare-ups of existing conditions like eczema and rosacea Delayed wound healing Heightened skin sensitivity Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs) When sugar molecules attach to proteins in your skin, they create harmful compounds called AGEs. This process: Damages collagen and elastin fibers Reduces skin elasticity Creates deep wrinkles Accelerates premature aging Causes uneven skin tone The Sugar-Acne Connection High sugar consumption triggers a cascade of hormonal responses that directly affect your skin: Insulin Spike: Consuming sugar rapidly increases blood glucose levels Hormone Disruption: Your body releases insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) Sebum Production: IGF-1 stimulates oil glands to produce excess sebum Bacterial Growth: Excess oil creates an environment where acne-causing bacteria thrive Research published in the Journal of Clinical Nutrition demonstrates that participants following high-glycemic diets experienced 87% more acne lesions compared to those maintaining low-sugar diets. Blood Sugar Fluctuations Unstable blood sugar levels create additional skin challenges: Compromised skin barrier function Reduced collagen production Impaired skin cell turnover Increased oxidative stress Slower skin healing Studies from the American Academy of Dermatology indicate that maintaining stable blood sugar levels through diet can reduce inflammatory skin conditions by up to 50% within three months. These biological responses to sugar consumption create a complex web of skin issues that can persist long after you've finished that sugary treat. Understanding these mechanisms helps explain why dermatologists increasingly recommend dietary modifications as part of comprehensive skincare. If you're looking for delicious yet healthier options, consider trying our sugar-free Motichoor Ladoo, made with pure ghee and no sugars, perfect for any occasion while being gentle on your health. Benefits of Reducing Sugar for Skin Health Reducing sugar intake triggers a cascade of positive changes in your skin's appearance and health. Research published in the Journal of Clinical Medicine demonstrates that participants who followed a low-sugar diet for 12 weeks experienced a significant reduction in skin inflammation markers. Key Improvements You'll Notice: Reduced redness and irritation Decreased frequency of breakouts More balanced skin tone Enhanced natural glow Smaller-appearing pores Your skin's recovery process accelerates when you cut back on sugar. Within 72-96 hours of reducing sugar consumption, many people report visible improvements in their skin's clarity. This rapid response occurs because your body's inflammatory responses begin to normalize. Long-term Benefits for Skin Health: The transformative effects of a low-sugar lifestyle become increasingly apparent over time: Enhanced Collagen Production Your skin maintains better elasticity Fine lines appear less pronounced Natural healing processes improve Balanced Oil Production Reduced shine in oily areas Better moisture retention More uniform skin texture Improved Barrier Function Stronger protection against environmental damage Better nutrient absorption Enhanced moisture retention Studies show that maintaining consistent blood sugar levels helps your skin cells function optimally. When you eliminate added sugars, your skin receives steady nourishment without the spikes and crashes that can trigger inflammation. The Science Behind Sugar-Free Success: Research from dermatological studies reveals that reducing sugar intake by 50% can lead to: 25% reduction in inflammatory markers 40% improvement in skin barrier function 30% increase in collagen production These benefits compound over time, creating lasting improvements in your skin's health and appearance. Your commitment to reducing sugar intake allows your skin to maintain its natural repair and regeneration processes without interference from sugar-induced inflammation. A low-sugar lifestyle supports your skin's ability to: Produce healthy new cells Maintain proper hydration levels Fight environmental damage Preserve natural collagen structures Balance oil production effectively Incorporating sugar-free alternatives into your diet, such as our keto-friendly almond flour cake or diabetic-friendly coconut cookies, can make this transition easier and more enjoyable. Practical Steps to Cut Out Sugar for Better Skin Health Breaking free from sugar requires a strategic approach and careful attention to your food choices. Hidden sugars lurk in unexpected places, making label reading an essential skill for your skin health journey. Master Label Reading Skills: Look for ingredients ending in "-ose" (glucose, fructose, sucrose) Watch for terms like "syrup," "nectar," or "concentrate" Check for natural sweeteners like agave, honey, or maple syrup Scan nutrition facts for "Added Sugars" content Pay attention to serving sizes listed on packages Common Hidden Sugar Sources: Pasta sauces and condiments Breakfast cereals and granola Yogurt and flavored dairy products Protein bars and energy drinks Dried fruits and fruit juices Pre-made smoothies and beverages Practical Sugar-Reduction Strategies: Prepare meals at home to control ingredients Keep sugar-free snacks readily available Replace sugary drinks with infused water Start your day with protein-rich breakfast Plan ahead for social events and dining out Your taste buds adapt to reduced sugar intake within 1-2 weeks. Many people report decreased sugar cravings after this initial adjustment period. Focusing on whole, unprocessed foods naturally limits sugar consumption while providing essential nutrients for skin health. Conclusion Your journey to radiant skin extends beyond topical treatments. A holistic approach to skincare combines mindful nutrition with effective skincare practices. The evidence speaks clearly - cutting out sugar improves skin health through multiple pathways: Reduced inflammation leads to clearer, calmer skin Decreased AGE formation helps maintain skin elasticity Lower insulin responses minimize acne breakouts Enhanced collagen production supports skin structure Your skin reflects your dietary choices. By choosing a low-sugar lifestyle, you're investing in long-term skin health. Start with small changes - swap sugary snacks for sugar-free sweets made with natural sweeteners or read ingredient labels carefully to avoid hidden sugars, terms like "sugar-free," "no added sugar," and "unsweetened" can often be confusing but understanding them is crucial for making informed choices. Stay consistent with your choices. The transformation might take time, but your future self will thank you for making this positive change. Your skin deserves the best care possible, both inside and out. Take this first step toward healthier, more radiant skin by reducing your sugar intake today. FAQs 1.Can cutting out sugar really improve my skin health? Yes, cutting out sugar can lead to significant improvements in your skin's appearance and overall health. Reducing sugar intake helps decrease inflammation in the body, which is linked to various skin issues such as acne and eczema. 2.What are the negative effects of sugar on skin health? Excessive sugar intake can cause inflammation, leading to skin conditions like acne, eczema, and rosacea. High sugar consumption also contributes to the formation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which accelerate premature skin aging. 3.How does a low-sugar diet benefit my skin? A low-sugar diet has been shown to reduce inflammation levels in the body, resulting in clearer and healthier-looking skin. Eliminating added sugars can also enhance skin texture, tone, and elasticity over time. 4.What practical steps can I take to cut out sugar for better skin health? To cut out sugar effectively, read labels carefully to identify hidden sources of sugar in packaged foods. Consider healthy alternatives to satisfy sweet cravings while maintaining your skin health goals. 5.Is a holistic approach important for skincare beyond just cutting out sugar? Absolutely! A holistic approach combines good nutrition with effective skincare practices. By focusing on both diet and skincare routines, you can achieve healthier and more radiant skin.

Do sugar-free products reduce the risk of diabetes?
Sugar-free products have become a staple in the daily lives of people managing diabetes and those seeking healthier alternatives. They promise the sweetness we crave without the blood sugar spikes associated with regular sugar consumption. Research suggests that sugar-free alternatives can play a role in diabetes management, yet their relationship with diabetes risk presents a complex picture. While these products don't directly raise blood glucose levels, their impact on metabolism and long-term health requires careful consideration. Remember: Sugar-free doesn't mean unrestricted consumption is safe. These products work best as part of a comprehensive diabetes management strategy, not as a standalone solution. Understanding Sugar-Free Products Sugar-free products have become a staple in diabetic diets, offering a way to enjoy sweet flavors without compromising blood sugar levels. These products contain zero or negligible amounts of natural sugar, replacing it with alternative sweetening compounds that provide sweetness without the caloric impact. Popular Natural and Artificial Sweeteners: Stevia: A plant-based sweetener 200-400 times sweeter than sugar, with zero calories and no effect on blood glucose. Xylitol: A sugar alcohol providing 40% fewer calories per g than sugar, with minimal impact on blood sugar levels Erythritol: Another sugar alcohol with 70% of sugar's sweetness but only 6% of its calories Monk Fruit: A natural sweetener 150-200 times sweeter than sugar, containing zero calories These sweeteners work differently in your body compared to regular sugar. Your digestive system either doesn't break them down or processes them differently, preventing blood sugar spikes common with regular sugar consumption. Benefits for Diabetic Management: Reduced caloric intake Better blood sugar control Easier weight management Decreased dental problems Satisfaction of sweet cravings without glucose impact The low-calorie nature of sugar-free products makes them particularly valuable for weight management - a crucial factor in diabetes control. You can reduce your daily caloric intake while maintaining the pleasure of sweet foods and beverages. These alternatives allow you to enjoy desserts, beverages, and other traditionally sugar-laden foods while keeping your blood glucose levels stable. Research shows that switching to sugar-free alternatives can lead to significant reductions in daily sugar intake, helping you maintain better control over your diabetes management goals. The variety of available options means you can find alternatives that suit your taste preferences and dietary needs. To further aid in diabetes management, it's also beneficial to increase dietary fiber intake. This nutrient plays an important role in stabilizing blood sugar levels. The Science Behind Artificial Sweeteners and Their Impact on Health Artificial sweeteners interact with your body in complex ways that scientists are still working to understand. Research reveals these sugar substitutes can trigger unexpected metabolic responses, despite their zero-calorie status. How Your Body Processes Artificial Sweeteners Your body processes artificial sweeteners differently from natural sugars. When you consume these substances, they bypass traditional metabolic pathways, potentially disrupting your body's learned responses to sweet tastes. This disruption can lead to: Altered insulin sensitivity Changes in glucose metabolism Unexpected hormonal responses The Role of Gut Microbiome Your gut microbiome plays a crucial role in this metabolic equation. Recent research indicates artificial sweeteners can: Reduce beneficial bacteria populations Alter microbial diversity Change bacterial metabolic functions These changes in gut bacteria composition can trigger inflammation and affect how your body: Processes nutrients Regulates blood sugar Maintains metabolic balance Scientists have observed that regular consumption of artificial sweeteners may lead to glucose intolerance in some individuals - a direct result of changes in gut bacterial communities. This finding suggests a potential link between sweetener use and metabolic health that extends beyond their zero-calorie status. Potential Effects on Other Bodily Systems The impact on your gut health can extend to other bodily systems, affecting: Immune function Mental health Energy metabolism Hormone production Exploring Healthier Alternatives Natural sweeteners offer a safer option compared to artificial ones, as they don't disrupt your gut microbiome or trigger unexpected metabolic responses. Sugar free sweets made with natural sweeteners do not have any effects on an individuals health. Discover our range of gut-friendly and diabetic friendly sweets to indulge guilt free. The Pros and Cons of Sugar-Free Products for Diabetes Management Sugar-free products offer distinct advantages for individuals managing diabetes: Benefits: Zero-calorie sweeteners help maintain stable blood glucose levels Reduced caloric intake supports weight management goals Lower sugar consumption decreases cardiovascular disease risk Research indicates that replacing sugar with artificial sweeteners can lead to a 5-10% reduction in daily caloric intake, supporting weight loss efforts crucial for diabetes management. For more on what replaces sugar in these products, you might find this article on decoding the sweet swap informative. Potential Drawbacks: Some sugar substitutes may trigger insulin response Artificial sweeteners can increase sugar cravings Certain sugar alcohols might cause digestive issues A 2022 study published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that participants who consumed sugar-free products showed improved glycemic control when combined with proper diet and exercise. The research demonstrated a 15% decrease in post-meal blood sugar spikes compared to regular sugar consumption. The American Heart Association recognizes sugar-free alternatives as part of a heart-healthy diet, noting their potential to reduce cardiovascular complications in diabetic patients. Studies show a correlation between sugar-free product consumption and decreased inflammation markers associated with heart disease. Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for diabetics who are incorporating sugar-free alternatives into their diet. Your glucose readings can reveal how different sugar substitutes, such as Erythritol, affect your body, helping you make informed decisions about which products work best for you. Balancing Sugar-Free Products with a Holistic Approach to Nutrition in Diabetes Management Strategies Sugar-free products are valuable tools in diabetes management, but they work best when combined with a comprehensive nutritional strategy. A balanced approach includes: Whole Foods Integration: Pair sugar-free alternatives with nutrient-dense whole foods like vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Portion Control: Practice mindful eating with both sugar-free and regular foods. Fiber-Rich Foods: Include foods high in fiber to help regulate blood sugar levels naturally. Smart Carbohydrate Choices: Select complex carbohydrates from sources like quinoa, sweet potatoes, and legumes. It's important to note that carbs are cheap, but they don't always have to be unhealthy. Natural Sugar Alternatives: Consider incorporating naturally sweet foods like berries and citrus fruits. Your dietary choices extend beyond sugar substitution. A well-rounded meal plan supports: Blood sugar stability Improved insulin sensitivity Better weight management Enhanced nutrient absorption Sustained energy levels Creating a balanced nutrition plan means thinking beyond sugar elimination. The focus shifts to building a sustainable eating pattern that nourishes your body while managing diabetes effectively. Make Informed Choices with Artinci's Sugar-Free Range Artinci's sugar-free product line offers a thoughtful selection of diabetic-friendly sweets designed to complement your balanced diet. Each product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets strict quality standards while maintaining delicious taste profiles. Key Features of Artinci's Sugar-Free Range: Natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit Zero artificial preservatives Low glycemic index ratings Complete nutritional transparency Portion-controlled packaging Your journey toward better blood sugar management can start with Artinci's carefully crafted alternatives to traditional sugary treats. These products help you satisfy your sweet cravings without compromising your health goals. Remember: While Artinci's sugar-free products can support your diabetes management journey, they work best as part of a comprehensive nutrition plan. Always consult your healthcare provider about incorporating new products into your diet. FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions) Do sugar-free products help reduce the risk of diabetes? While sugar-free products can support diabetes management by helping control blood sugar levels, they should be consumed mindfully and in moderation. They are not a guaranteed solution for reducing diabetes risk. What are common types of artificial sweeteners found in sugar-free products? Common artificial sweeteners include stevia, xylitol, erythritol, and monk fruit. These sweeteners provide low-calorie options that can aid in blood sugar control and weight management for diabetics. How do artificial sweeteners impact metabolism and appetite regulation? Artificial sweeteners can affect metabolism and may play a role in regulating appetite and cravings. However, their effects can vary among individuals, and it's essential to monitor personal responses. What are the potential risks of consuming too many sugar-free products? Excessive consumption of sugar-free products may lead to negative health outcomes, such as altered taste preferences that encourage unhealthy food choices. Some studies have also linked high diet soda intake to metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Why is regular blood sugar monitoring important for diabetics using sugar-free alternatives? Regular blood sugar monitoring is crucial for diabetics using sugar-free alternatives to ensure that these products are effectively supporting their health goals. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice is also recommended. How can I incorporate sugar-free products into a balanced diet for diabetes management? To effectively manage diabetes, combine sugar-free products with other healthy dietary choices. Emphasizing a balanced diet alongside mindful consumption of these alternatives can lead to better overall health outcomes.

Are Honey and Jaggery Better Than Artificial Sweeteners?
Introduction Many people are looking for healthier options to replace refined sugar, which has led to a growing interest in both natural and artificial sweeteners. Health-conscious consumers are turning to alternatives like honey and jaggery, which have gained popularity in the market. To make informed dietary choices, it's important to understand how different sweeteners affect our health. While natural sweeteners such as honey and jaggery are often seen as better options, they may have surprising effects on blood sugar levels. By examining the science behind these sweeteners, we aim to help you make decisions that align with your health goals. Natural Sweeteners: Honey and Jaggery Natural sweeteners have gained significant attention as alternatives to refined sugar. Let's explore two popular options that have been used for centuries in traditional medicine and cooking. 1. Honey Raw honey is a remarkable natural sweetener packed with bioactive compounds. Its composition includes: 38% fructose 31% glucose 17% water 7% maltose Various enzymes, amino acids, and minerals The unique enzyme content in honey, including glucose oxidase and invertase, contributes to its health-promoting properties. These enzymes aid in the breakdown of complex sugars and support digestive health. Raw honey contains essential nutrients: Vitamins: B6, thiamin, riboflavin, pantothenic acid Minerals: Calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, manganese Antioxidants: Flavonoids and phenolic compounds The antimicrobial properties of honey make it valuable for wound healing. Its high sugar content and low pH create an environment where bacteria cannot thrive. Medical-grade honey is used in clinical settings to treat burns, ulcers, and other wounds. Research shows honey's potential benefits: Natural cough suppressant Immune system support Gut health improvement Skin healing properties It's important to note that despite these benefits, honey still impacts blood sugar levels significantly and should be consumed mindfully, especially by people monitoring their glucose intake. 2. Jaggery Jaggery is a traditional non-centrifugal sugar made from the concentrated sap of sugar cane or palm trees. It is produced using a natural processing method that involves slow heating and reduction, which helps retain the essential minerals and nutrients that are lost in refined sugar processing. This golden-brown sweetener is packed with nutrients, including: Iron (10mg per 100g) Calcium (80mg per 100g) Magnesium Potassium B-vitamins However, it's important to note that jaggery still has a significant impact on blood sugar levels. Its glycemic index ranges from 84 to 86, which means it can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar - something that people with diabetes need to be cautious about. In fact, a single serving (10g) of jaggery contains approximately: 9.8g of sugar 38 calories 0g fiber 0.01g protein Even though jaggery contains minerals and antioxidants, it also has a high sugar content. This means that portion control is crucial for maintaining a balanced diet and managing blood sugar levels. Comparing Natural Sweeteners with Artificial Sweeteners Artificial sweeteners are synthetic sugar substitutes designed to provide sweetness without calories. These lab-created compounds include aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin, commonly found in diet sodas, sugar-free candies, and processed foods. Here's a comparison between natural and artificial sweeteners: Sweetener Type Sugar Content Calories Health Impact Blood Sugar Response Honey 17g/tbsp 64/tbsp Contains antioxidants, minerals Rapid spike Jaggery 16g/tbsp 62/tbsp Rich in iron, minerals Moderate spike Aspartame 0g 0 Potential headaches, digestive issues No spike Sucralose 0g 0 May alter gut bacteria Minimal spike Stevia 0g 0 Natural plant-based, few side effects No spike Note: Values are approximate and may vary based on brand and processing methods Glycemic Index and Blood Sugar Responses The glycemic index (GI) measures how quickly foods raise blood sugar levels. A lower GI (below 55) indicates slower digestion and steadier blood sugar levels - crucial for diabetes management. Here's how different sweeteners rank on the GI scale: High GI (70+) Jaggery: 84-86 Regular sugar: 65-70 Honey: 58-61 Low GI (55 or less) Stevia: 0 Monk fruit: 0 Sucralose: 0 Sugar alcohols (xylitol, erythritol): 0-7 While natural sweeteners like honey and jaggery contain beneficial nutrients, their high GI can cause rapid blood sugar spikes. Artificial sweeteners and natural zero-calorie options like stevia maintain stable blood sugar levels, making them suitable choices for people managing diabetes. Healthy Dessert Alternatives Looking for delicious sugar-free treats that won't compromise your health goals? Explore our sugar-free desserts collection for guilt-free indulgence. From stevia-sweetened cookies to monk fruit-based cakes, discover a world of naturally sweetened delights. Check out our diabetic-friendly desserts and weightloss collections for more options that fit your lifestyle. These desserts work well for people watching their sugar intake or managing diabetes, offering satisfying alternatives to conventional sweets. Start your sugar-free journey today! Incorporating Natural Sweeteners in Desserts Natural sweeteners can transform traditional desserts into healthier treats. Here's how to use them effectively: Honey in Baking: Replace sugar with ¾ cup honey for every 1 cup sugar Reduce liquid ingredients by ¼ cup per cup of honey Lower oven temperature by 25°F to prevent over-browning Jaggery Tips: Powder jaggery finely before using in recipes Use 1:1 ratio when substituting for sugar Add a pinch of baking soda to balance the pH Note: Natural sweeteners add unique flavors to desserts - honey brings floral notes, while jaggery adds caramel undertones; however, keep in mind that jaggery and honey still spike your sugar levels. To keep your blood sugar levels in check, try using natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit. Choosing Sweeteners Wisely: The Bottom Line The choice between honey, jaggery, and artificial sweeteners isn't a one-size-fits-all decision. Each option brings unique benefits and considerations to the table. For individuals managing diabetes: Artificial sweeteners might offer better blood sugar control, despite their controversial nature. For those seeking nutritional benefits: Natural sweeteners like honey and jaggery provide essential minerals and compounds, yet their sugar content demands mindful consumption. The key lies in understanding your personal health needs and using sweeteners strategically. Consider: Your current health status Blood sugar sensitivity Nutritional requirements Intended use (baking, beverages, or direct consumption) Make your choice based on these factors rather than following general assumptions about what's "healthier." FAQs 1.What are the main differences between honey, jaggery, and artificial sweeteners? Honey and jaggery are natural sweeteners derived from plants, while artificial sweeteners are synthetic. Honey contains glucose and fructose, offering nutritional benefits like enzymes and vitamins. Jaggery is made from sugar cane or palm sap and is rich in minerals like iron and calcium. In contrast, artificial sweeteners have little to no calories but may have adverse health impacts. 2.How do honey and jaggery impact blood sugar levels compared to artificial sweeteners? Honey has a lower GI than sugar, but jaggery has a similar or even higher GI. This means honey causes a slower rise in blood sugar levels. However, it still contains calories and sugars that can affect diabetics. Artificial sweeteners often do not raise blood sugar levels but may have other health implications. 3.Why is jaggery considered healthier than refined sugar? Jaggery is considered healthier than refined sugar because it retains more nutrients during processing. It contains essential minerals such as iron, calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which are beneficial for health but are found in minute quantities. 4.Can I use honey or jaggery in baking healthy desserts? Yes! Honey and jaggery can be excellent alternatives to refined sugar in baking. They not only add sweetness but also enhance the nutritional value of desserts like sugar-free biscuits or cakes. However, they might not be the best option for diabetics. 5.What should I consider when choosing between natural and artificial sweeteners? When choosing between natural and artificial sweeteners, consider your health goals, dietary needs (especially if diabetic), and any potential side effects associated with artificial options. Natural sweeteners like honey and jaggery offer additional nutrients but still contain sugars, while artificial sweeteners provide low-calorie options but may come with health concerns.

How Does Sucralose Compare to Natural Sweeteners?
Introduction With so many sugar alternatives available today, it can be hard to figure out which one is right for you. Sucralose, a widely used artificial sweetener found in many sugar-free products, is often compared to various natural sweeteners. Each option has its own unique qualities and advantages. By understanding the differences between sucralose and natural sweeteners, you can make better choices about your diet and health. Whether you're managing diabetes, trying to reduce your calorie intake, or simply looking for healthier substitutes for sugar, knowing how these sweeteners stack up against each other can greatly influence your food choices. In this guide, we'll explore the world of sweeteners in detail. We'll look at where they come from, how they taste, their effects on health, and how you can use them in your everyday cooking and baking. What is Sucralose? Sucralose, commonly known by the brand name Splenda, is an artificial sweetener created through chemical modification of regular table sugar (sucrose). Scientists discovered this zero-calorie sweetener in 1976 by replacing three hydrogen-oxygen groups in the sugar molecule with chlorine atoms. The production process involves a multi-step laboratory procedure that transforms sucrose into a substance 600 times sweeter than regular sugar. This intense sweetness means only tiny amounts are needed to achieve the same level of sweetness as sugar. Unlike natural sugar, sucralose: Passes through the body without being broken down Contains zero calories Maintains stability at high temperatures Remains shelf-stable for extended periods The FDA approved sucralose for general use in 1999, making it one of the most widely used artificial sweeteners in processed foods, beverages, and as a tabletop sweetener. What Are Natural Sweeteners? Natural sweeteners are sweet substances that come from plants and are minimally processed to retain their natural form. Unlike artificial sweeteners, which may contain synthetic chemicals or artificial ingredients, natural sweeteners offer a sweet taste derived entirely from nature. Some Common Examples of Natural Sweeteners Include: Stevia: This zero-calorie sweetener is extracted from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant and is known to be 200-400 times sweeter than sugar. Monk Fruit: Derived from the Siraitia grosvenorii fruit, monk fruit sweetener provides sweetness without any calories. Erythritol: A naturally occurring sugar alcohol found in various fruits, erythritol offers about 70% of the sweetness of sugar but with very few calories. Natural sweeteners have nutritional benefits that artificial sweeteners do not possess. Many of them contain antioxidants and other beneficial compounds that promote good health. For example, stevia contains steviol glycosides which may help regulate blood sugar levels, while monk fruit is rich in unique antioxidants called mogrosides. These plant-based alternatives can be used in a variety of ways such as baking, adding to beverages, or as table sweeteners. This versatility makes them appealing options for health-conscious individuals who are looking for natural substitutes for sugar. Comparison of Sucralose and Natural Sweeteners Understanding the fundamental differences between sucralose and natural sweeteners starts with their distinct origins. Let's explore how these sweeteners come to life through vastly different processes. 1. Origin and Source The journey from raw material to sweetener reveals a stark contrast between sucralose and natural alternatives. Sucralose emerges from a complex laboratory process where scientists modify regular sugar molecules. This synthetic creation involves replacing three hydrogen-oxygen groups with chlorine atoms, resulting in a substance 600 times sweeter than traditional sugar. Natural sweeteners tell a different story: Stevia grows as a leafy plant in South America, where indigenous people have used its sweet leaves for centuries Monk Fruit comes from a small round fruit native to southern China Yacon Syrup derives from the roots of the yacon plant found in the Andes Mountains The production methods also differ significantly: Sucralose: Requires chemical synthesis in controlled laboratory conditions Natural Sweeteners: Involve extraction processes that preserve the plant's natural compounds This distinction in sourcing reflects in the products' marketing and consumer perception. While sucralose represents modern food science's capability to create efficient sweetening agents, natural alternatives appeal to those seeking minimally processed options aligned with traditional food sources. 2. Sweetness and Taste Profile The sweetness intensity between sucralose and natural sweeteners varies significantly. Sucralose stands out with its remarkable sweetness - 600 times sweeter than table sugar. In comparison, stevia ranges from 200-400 times sweeter, while monk fruit delivers 150-200 times the sweetness of sugar. Each sweetener brings a distinct taste experience: Sucralose: Clean, sugar-like taste with minimal aftertaste Stevia: Natural sweetness with potential licorice notes and slight bitter finish Monk Fruit: Fruity sweetness with a subtle caramel undertone Consumer preferences often lean toward sucralose in beverages and baked goods due to its sugar-like taste. Natural sweeteners shine in specific applications - stevia pairs well with dairy products, while monk fruit enhances fruit-based desserts and smoothies. 3. Impact on Blood Sugar Levels and Diabetes Management Both sucralose and natural sweeteners offer promising options for blood sugar management in diabetic individuals. Research indicates sucralose doesn't significantly affect blood glucose or insulin levels, however some studies show that it may effect gut health. Natural sweeteners like stevia show additional benefits: Potential improvement in insulin sensitivity Reduced post-meal blood sugar spikes Support for healthy glucose metabolism The zero-calorie nature of both options allows people with diabetes to enjoy sweet treats without compromising their blood sugar control. 4. Safety, Health Concerns, and Regulatory Approval The FDA has thoroughly assessed the safety of sucralose through extensive testing. After decades of research, it was approved in 1999, with studies confirming that it remains stable during cooking and storage. The established Acceptable Daily Intake (ADI) allows for 23 packets of sucralose per day. Potential Gut Health Effects Recent studies have raised concerns about the impact of sucralose on gut health. Research published in the Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health suggests that sucralose may disrupt the composition of beneficial gut bacteria. Scientists observed changes in the microbiome after regular consumption of sucralose. Comparison with Natural Sweeteners Natural sweeteners such as stevia have received FDA's "Generally Recognized as Safe" (GRAS) status, with an ADI allowing for 27 packets per day. Long-term studies indicate minimal side effects, although some users report mild digestive discomfort when consuming large amounts. The regulatory landscape is continuously evolving as new research emerges regarding the long-term effects of both synthetic and natural sweeteners on human health. Benefits of Natural Sweeteners for Diabetics Natural sweeteners are great for making tasty desserts that are safe for diabetics without affecting blood sugar levels. Various desserts like cookies, cakes and Indian sweets can be made using natural sweeteners without compromising their taste. These natural alternatives allow people with diabetes to enjoy sweet treats while maintaining stable blood glucose levels. But natural sweeteners aren't just for desserts - they can also be used in: Morning coffee or tea Homemade salad dressings Baked goods Yogurt parfaits Natural sweeteners offer a delicious taste and health benefits, making them a great choice for anyone with diabetes or following a low-sugar diet. FAQs What is sucralose and how is it produced? Sucralose is an artificial sweetener commonly known by the brand name Splenda. It is created through a chemical modification process that transforms sugar into a zero-calorie sweetener, making it much sweeter than regular sugar. What are natural sweeteners and can you give some examples? Natural sweeteners are derived from plants and include options like stevia, monk fruit, and erythritol. These sweeteners are often chosen for their nutritional benefits compared to synthetic alternatives. How does the sweetness of sucralose compare to natural sweeteners? Sucralose is approximately 600 times sweeter than sugar, while natural sweeteners like stevia and monk fruit also provide significant sweetness but with varying levels of intensity. This difference affects consumer preferences in taste. What impact do sucralose and natural sweeteners have on blood sugar levels? Sucralose does not raise blood sugar levels, making it a suitable option for diabetics. In contrast, some natural sweeteners like stevia may also help manage blood sugar levels, providing additional benefits for those with diabetes. Are there any health concerns associated with sucralose? While sucralose has been approved by regulatory bodies like the FDA, some studies suggest potential health concerns related to gut microbiota. It's important to weigh these considerations against the benefits of using this artificial sweetener. What are the advantages of using natural sweeteners in diabetic diets? Natural sweeteners offer several benefits for diabetics, including lower calorie content and potential positive effects on blood sugar management. They can be used in various recipes for diabetic-friendly desserts and low-sugar foods.