Welcome to the world of sugar free joy!
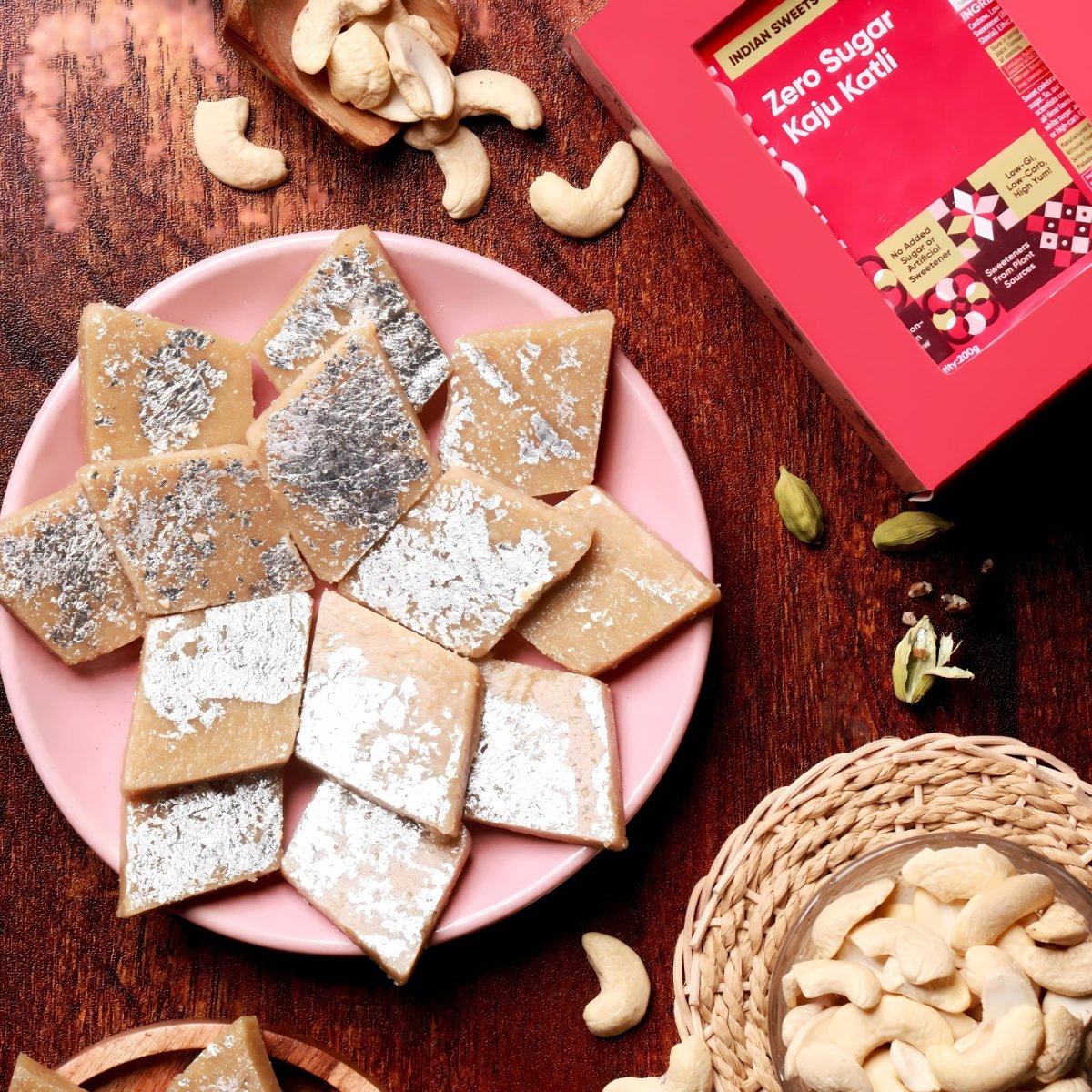
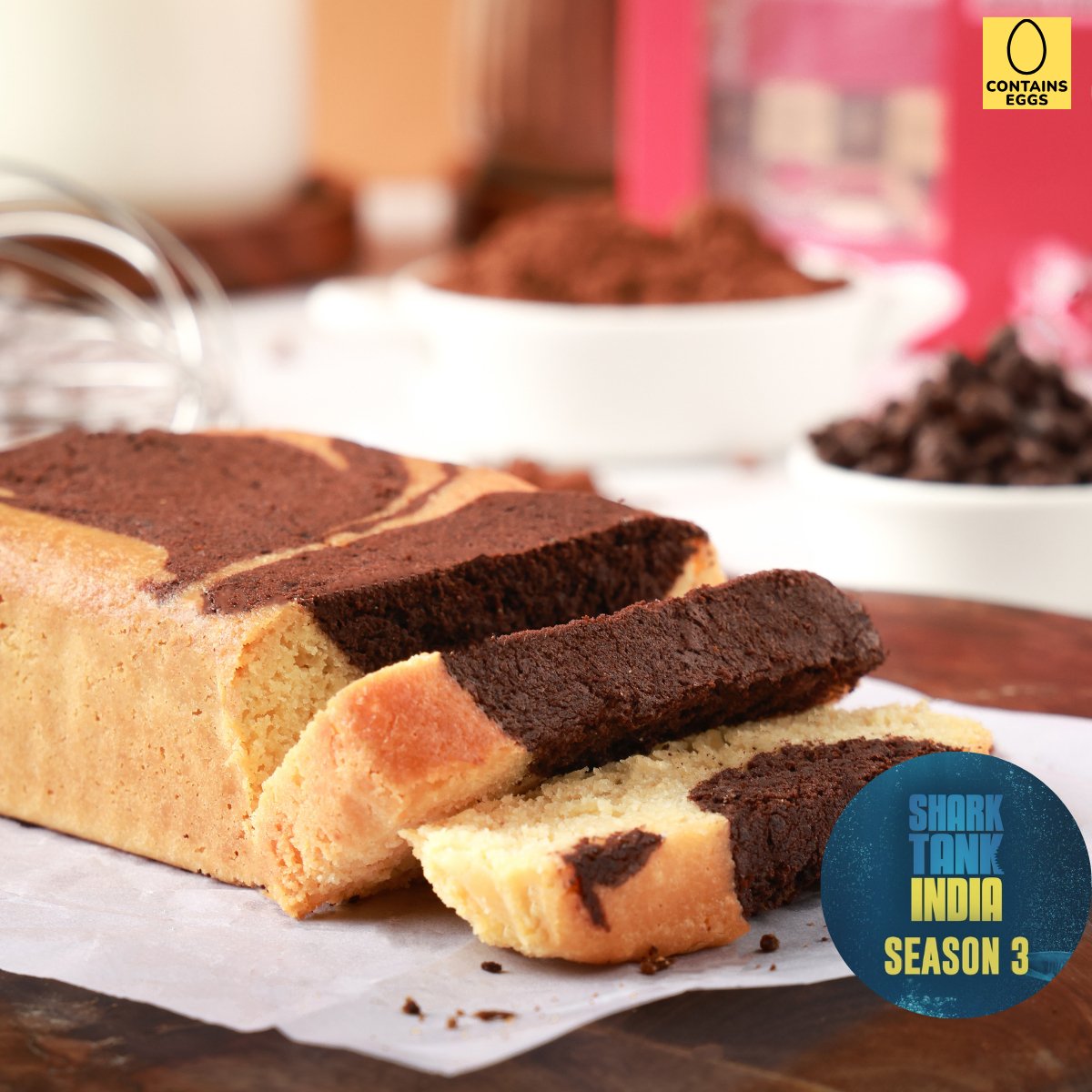
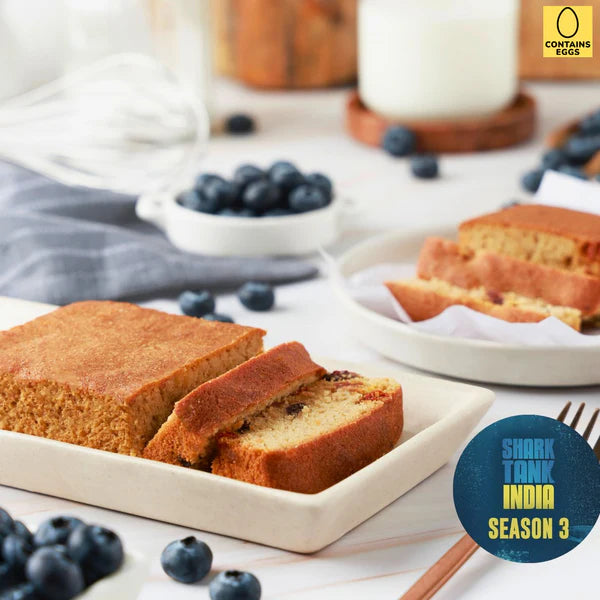
Low Carb Sugar-Free Sweets & Cakes
Artinci was born out of Aarti's and Sumit's (Artinci's founders) abiding love for great-tasting dessert, while helping them stay committed to their health goals as well. As a result, Artinci makes delicious desserts with zero sugar, that are science and evidence-backed.
Aarti and Sumit come from a family of three generations of diabetics. They were themselves diagnosed pre-diabetic in 2012, and right there began a lifelong quest of a healthy, active lifestyle, including healthy swaps in food
Sugar free Sweets & Cakes

Aarti Laxman (Founder)
Artinci is founded by Aarti Laxman, a certified Metabolic coach in the Low-Carb Nutrition & Metabolic Health domain from dLife.in, India’s only legally tenable course in this subject—recognized by the NSDC (under the Ministry of Skill Development & Entrepreneurship, Govt. of India). It’s also internationally accredited by the CPD Standards Office UK, with a global record of 144 CPD hours—the highest for any course of its kind. The accreditation is both nationally valid and globally recognised in over 50+ countries..
Festive Gifting in Artinci
Let customers speak for us
All about Sugar and sugar-free

घी और मक्खन में सैचुरेटेड फैट प्रमुख होता है, लेकिन इनके MUFA-PUFA अनुपात से इंसुलिन रेसिस्टेंस और टाइप-2 डायबिटीज रिस्क बदलता है। सीमित मात्रा में घी बेहतर विकल्प साबित हो सकता है, जबकि अधिक सेवन हृदय जोखिम बढ़ाता है। फैट ब्रेकडाउन: घी बनाम मक्खन घी में सैचुरेटेड फैट ~60%, MUFA ~30%, PUFA ~5% होता है—यह ब्यूटिरिक एसिड से गट हेल्थ सुधारता है। मक्खन में SFA 51%, ट्रांस फैट 3% और लैक्टोज़ मौजूद रहता है, जो डायबिटिक्स के लिए पाचन समस्या पैदा कर सकता है। प्रति 100g: घी 900 kcal, मक्खन 717 kcal। फैट प्रकार घी (%) मक्खन (%) डायबिटीज प्रभाव SFA 60 51 अधिकता से रिस्क ↑ MUFA 30 25 इंसुलिन सुधार PUFA 5 4 संतुलन जरूरी टाइप-2 डायबिटीज रिस्क पर SFA का असर उच्च SFA (घी/मक्खन) से इंसुलिन रेसिस्टेंस 10-20% बढ़ सकता है, लेकिन घी का CLA फैट मेटाबॉलिज्म बेहतर करता है। स्टडीज दिखाती हैं SFA से HbA1c स्थिर रहता है यदि <10g/दिन। अधिक सेवन LDL बढ़ाकर हृदय जोखिम पैदा करता है। MUFA-PUFA का भूमिका घी के MUFA (ओलेइक एसिड) इंसुलिन सेंसिटिविटी बढ़ाते हैं, जबकि कम PUFA ऑक्सीडेशन रोकता है। मक्खन में असंतुलित PUFA ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स बढ़ा सकता है। डायबिटिक्स को SFA:MUFA 1:1 रखना चाहिए—घी रोटेशन में सरसों तेल मिलाएं। प्रैक्टिकल टिप्स भारतीय थाली के लिए सुबह ½ चम्मच घी खाली पेट लें—ट्राइग्लिसराइड्स कंट्रोल रहेंगे। मक्खन ब्रेड पर न लगाएं; डाल/सब्ज़ी में घी तड़का करें। पोस्ट-मील ग्लूकोज़ <140 रखें, HbA1c चेक करवाएं। कुल फैट 20-25ml/दिन। https://nesr.usda.gov/what-effect-saturated-fat-intake-increased-risk-cardiovascular-disease-or-type-2-diabetes https://www.abplive.com/lifestyle/ghee-vs-butter-what-is-better-in-terms-of-your-health-know-conclusion-1795196 https://continentalhospitals.com/blog/is-ghee-safe-for-heart-diabetes-and-weight-issues/ https://www.dainikjagranmpcg.com/life-style/desi-ghee-vs-butter-is-right-for-health/article-31797

“Grass-Fed Ghee, Normal Butter Aur Refined Oils: Insulin Resistance, Triglycerides Aur HbA1c Par Asar”
Ghee from grass-fed cows offers unique benefits over regular butter and refined oils for diabetes management due to its nutrient profile. These fats influence insulin sensitivity, blood triglycerides, and long-term HbA1c differently based on their composition and processing. Moderation remains key across all options. Nutrient Breakdown Grass-fed ghee excels with higher conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) at 2-5x levels compared to grain-fed butter, aiding fat metabolism and reducing insulin resistance. Normal butter has similar saturated fats (about 50%) but less antioxidants, while refined oils like sunflower are stripped of vitamin E, promoting oxidative stress that elevates triglycerides 20-30%. Fat Source Key Nutrients Insulin Impact Grass-Fed Ghee CLA, Butyric Acid, Vitamin A Improves sensitivity Normal Butter Vitamin A, Saturated Fats Neutral, lactose concerns Refined Oils Omega-6, Minimal Antioxidants Worsens resistance Effects on Insulin Resistance Grass-fed ghee's short-chain fatty acids support gut health, potentially lowering insulin resistance markers by 10-15% in studies on high-fat diets. Refined oils' high omega-6 ratio (20:1 vs ideal 4:1) fuels inflammation, impairing insulin signaling. Butter sits neutral but lacks ghee's stability at high heat, avoiding harmful aldehydes. Triglycerides and HbA1c Impact Refined oils correlate with 15-25% higher triglycerides due to polyunsaturated fat oxidation during cooking, indirectly raising HbA1c. Grass-fed ghee shows neutral-to-positive effects on lipids, with CLA reducing fat storage. Butter moderately raises LDL if overconsumed, but all three maintain stable HbA1c when limited to 10-15g daily alongside low-GI carbs. Practical Recommendations Rotate grass-fed ghee for tadka or roti (1 tsp/meal) to leverage its smoke point (485°F) over butter (350°F). Avoid refined oils for frying; opt for them cold. Track post-meal glucose: aim for <140 mg/dL spikes. Pair with exercise for optimal insulin sensitivity. https://continentalhospitals.com/blog/is-ghee-safe-for-heart-diabetes-and-weight-issues/ https://asmitaorganicfarm.com/blogs/aof/ghee-is-good-for-diabetes-how-to-consume-ghee https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/life-style/food-news/oil-vs-ghee-vs-butter-which-is-the-healthier-choice-for-cooking-and-wellness/articleshow/125205878.cms

“Kya Ghee Diabetics Ke Liye Safe Hai? Glycemic Index, Insulin Sensitivity Aur Daily Limit”
घी का ग्लाइसेमिक इंडेक्स: ब्लड शुगर पर असर घी शुद्ध वसा है जिसमें कोई कार्बोहाइड्रेट नहीं, इसलिए इसका GI 0 है—यह चावल या रोटी की तरह शुगर स्पाइक नहीं पैदा करता। स्टडीज दिखाती हैं कि सफेद चावल में थोड़ा घी मिलाने से GI कम हो जाता है, क्योंकि घी पाचन धीमा करता है। डायबिटीज रोगी पोस्ट-मील ब्लड शुगर (<140 mg/dL) बनाए रखने के लिए घी को carbs के साथ मिलाकर खा सकते हैं। इंसुलिन सेंसिटिविटी पर घी का प्रभाव घी में ब्यूटिरिक एसिड और CLA जैसे तत्व गट हेल्थ सुधारते हैं, जो इंसुलिन रेसिस्टेंस कम कर सकता है। आयुर्वेदिक दावों के अनुसार, गाय का घी अग्नि बढ़ाता है और प्रोसेस्ड फैट से बेहतर है, लेकिन मॉडर्न स्टडीज अधिक सेवन को LDL कोलेस्ट्रॉल बढ़ाने से जोड़ती हैं। डायबिटीज में घी से GLP-1 हार्मोन रिलीज हो सकता है, जो भूख कंट्रोल करता है। डेली लिमिट और प्रैक्टिकल टिप्स डायबिटीज रोगियों के लिए 10-15 ग्राम (1-2 चम्मच) घी रोज़ सुरक्षित है—सुबह खाली पेट या सब्ज़ी/दाल में मिलाएं। अधिक घी से सैचुरेटेड फैट (60%) बढ़ सकता है, जो टाइप-2 डायबिटीज रिस्क 10-20% तक प्रभावित करता है। घी घास-चरने वाली गाय का चुनें, रिफाइंड ऑयल के साथ न मिलाएं, और HbA1c चेक करवाएं। भारतीय किचन में घी के स्मार्ट उपयोग रोटी/खिचड़ी में ½ चम्मच घी डालें—यह सैटिएटी बढ़ाता है और ओवरईटिंग रोकता है। डीप फ्राई से बचें; हल्का तड़का या चाय में डालें। मूंगफली तेल के साथ रोटेट करें। वजन घटाने वाले डायबिटिक्स के लिए घी MCTs प्रदान करता है, लेकिन कुल कैलोरी 20% से कम रखें।

पाम ऑयल के डायबिटीज-अनुकूल विकल्प: भारतीय किचन के लिए सबसे अच्छे तेल
पाम ऑयल सैचुरेटेड फैट से भरपूर होता है, जो बार-बार गर्म करने पर इंसुलिन रेसिस्टेंस बढ़ा सकता है। डायबिटिक्स के लिए मोनो/पॉलीअनसैचुरेटेड फैट वाले तेल बेहतर हैं—ये ब्लड शुगर स्थिर रखते हैं और हृदय स्वस्थ बनाए रखते हैं। पाम ऑयल क्यों अवॉइड करें? उच्च सैचुरेटेड फैट (50%)। डीप फ्राई (समोसा, नमकीन) में ट्रांस फैट्स बनते हैं। स्टडीज दिखाती हैं कि ये इंसुलिन सेंसिटिविटी 20-30% कम कर सकते हैं। प्रोसेस्ड फूड्स (बिस्किट, मैगी) में छुपा खतरा। टॉप 5 विकल्प (डायबिटीज के लिए) तेल मुख्य लाभ उपयोग सावधानी सरसों का तेल (Mustard Oil) ओमेगा-3, एंटीऑक्सीडेंट। ब्लड शुगर कंट्रोल। तड़का, सब्जी। कच्चा न खाएं। मूंगफली का तेल (Peanut Oil) MUFA+PUFA, विटामिन E। LDL कम। फ्राई, करी। मॉडरेशन। राइस ब्रान ऑयल (Rice Bran Oil) ओरिजेनॉल, कोलेस्ट्रॉल ↓। हार्ट+शुगर फ्रेंडली। डीप फ्राई। तिल के साथ मिक्स। तिल का तेल (Sesame Oil) एंटी-इंफ्लेमेटरी, विटामिन E। तड़का, सलाद। हल्का गर्म। जैतून का तेल (Olive Oil) MUFA, इंसुलिन सेंसिटिविटी ↑। कच्चा/हल्का पकाना। हाई हीट न। रोजाना रोटेशन प्लान (सप्ताह भर) सोम-बुध: सरसों (PUFA हाई) मंगल-शुक्र: मूंगफली/राइस ब्रान (फ्राई) शनि-रवि: तिल/जैतून (हल्का)कुल तेल: 3-4 चम्मच/दिन (20-25ml)। बदल-बदलाव से ऑक्सीडेशन रिस्क कम। प्रैक्टिकल टिप्स लेबल चेक: "Partial Hydrogenated Palm Oil" = नो। स्टोरेज: ठंडी-अंधेरी जगह, 3 महीने में खत्म। टेस्टिंग: पोस्ट-मील ब्लड शुगर चेक करें। स्पाइक >140? तेल बदलें। बेस्ट कॉम्बो: 50% सरसों + 50% राइस ब्रान।नारियल तेल सीमित (MCTs अच्छे, लेकिन सैचुरेटेड हाई)। डायबिटीज में तेल मात्रा > प्रकार महत्वपूर्ण। 500ml मासिक खरीदें, क्वालिटी प्राथमिकता। HbA1c चेक करवाएं। https://www.healthshots.com/hindi/preventive-care/cook-food-in-these-5-cooking-oil-to-control-sugar-level-in-diabetes-patients/ https://www.jansatta.com/explained/these-are-the-best-and-worst-cooking-oil-for-diabetes-blood-sugar-patients-according-to-doctor/2584848/